The technique used to insert breast implants is more often than not decided by the plastic surgeon but that doesn’t mean you don’t have an input. Your surgeon may ask you some questions about your lifestyle, how active you are and also consider the shape and size of your desired implants in order to make the best decision. As part of our Breast Augmentation Video Guide we decided to help clear up some of the confusion around breast implants and Consultant Plastic Surgeon, Mr Adrian Richards goes through the most common incision sites and implant positions.
Where will the breast implant scar be?
The incision refers to the area in which the implant is inserted. This is important to you as it will determine where your scar will be. There are 4 different ways of inserting implants;
Inframammary crease
The inframammary crease or fold is the most popular incision technique used. The incision is made where the breast meets your chest wall, meaning that the scar will be hidden beneath the implant.
It also allows the surgeon to have good access to the breast tissue, they are able to control the fold or height of the implant and they are able to accurately place the implant without excessive handling of it.
Armpit
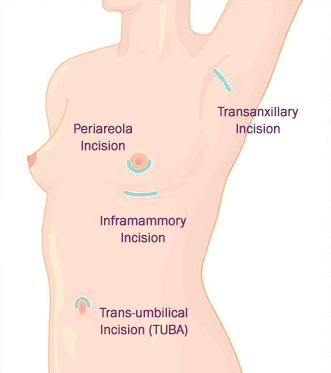
The armpit technique is often referred to as the ‘Transanxillary Incision’ and it is used for those trying to avoid a scar in the breast area. The tissue within the armpit is known for healing well often leaving a scar that is virtually undetectable. The incision is made within one of the natural creases of the armpit; a channel is then created to the breast in which the implant will travel. In most cases, an endoscope (a small tube with a light and camera) is used so that the surgeon can see within the breast.
It is not a preferred method of working for plastic surgeons as it requires them to work further away from the breast making it difficult to get the implant in the right position and it may be difficult to find someone who performs breast augmentation under this method.
Nipple
The nipple incision is also known as a ‘Periareolar incision’ but it is important to note that the incision is not made in the nipple; the incision will instead be made around the edge of the areola. Once the incision is made the surgeon can then create a pocket for the implant to sit within before inserting the implant to sit centred behind the nipple.
The visibility of the scar can vary from patient to patient which is the main reason why your surgeon may advise against this option and for those that are concerned about breastfeeding and nipple sensitivity post-procedure then this technique may not be suitable.
Belly button
The belly button incision is also known as the ‘trans-umbilical breast augmentation’ or ‘TUBA’. The technique was invented in 1991 by Dr Gerald Johnson and it involves a small incision being made within the belly button and an endoscope is inserted which creates a track for the implant to be inserted along. Once the pocket has been created, a deflated saline implant is then inserted via the belly button up towards the breast pocket and once it is in the correct location the surgeon will then need to fill the implant up to the required size with saline which is again fed into the implant via the navel.
This method of inserting implants is difficult due to the fact that the surgeon is working so far from the actual breast getting the implant in the correct position is tricky and only a blow-up saline style implant can be used. This technique is not commonly performed in the UK and you should only be using a surgeon who has performed this incision method on a regular basis in order to get the best results.
The next decision your surgeon will make is whether to place your implants under or over the muscle. Different surgeons will have different preferences but ultimately this is down to your own breast measurements alongside your lifestyle.
Will the breast implant be under or over the muscle?
Under
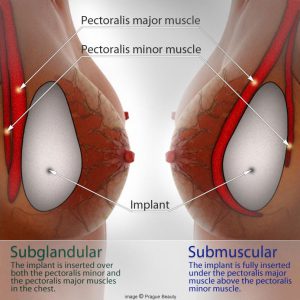
If you do not have enough natural breast tissue then the best option is usually to place your implant under the muscle. However placing the implant completely under the muscle is not commonly done anymore and it may be the case that technically your implant is being placed half under the muscle, this is more commonly known as dual plane or partial under the muscle. A dual plane technique means that your implant is placed beneath the pectoralis major muscle but it is only partially behind the muscle and partially behind the breast gland.
Front
If you have sufficient breast tissue then you would be suitable for your implants to be placed in front of the muscle known as subglandular. Implants placed in front of the muscle are placed over the pectoralis minor and pectoralis major muscles within the chest.
There are pros and cons to each position all of which can be discussed with your surgeon or more information can be found here.
So why choose The Private Clinic for Breast Augmentation Surgery?
- Our breast surgeons are experts in their field and have carried out thousands of breast enlargement operations.
- We have a 24-hour patient helpline to ensure you are always in the best of hands.
- As many post-operative care and appointments with your surgeon and nursing team as required.
- Three years cover for all surgical, hospital and nursing care, in case of any medical issue giving you peace of mind.
- Lifetime guarantee on Nagor implants for rupture and capsular contracture.
- The Private Clinic offers a unique warranty of £1000 towards surgical costs in case of rupture for 10 years from the date of your operation.
- Comprehensive Breast enlargement Patient Guide.
- Outstanding hospital facilities.
- Our excellent reputation for patient safety, satisfaction, honest advice and outstanding care means your journey with The Private Clinic will be an exciting experience to a new found shape.
Consultations for breast augmentation surgery are available at London Harley Street, Birmingham, Bristol, Glasgow, Manchester, Leeds, Northampton and Buckinghamshire with our team of expert consultant plastic surgeons;
- Mr Adrian Richards, MBBS, MSc, FRCS (Plast.) GMC Number: 3286812
- Mr Navid Jallali BSc MB ChB (Hons) MD FRCS (Plast) GMC Number: 4404969
- Mr Dario Rochira BS, MD GMC Number: 6130664
- Mr Davood Fallahdar FRCS (Plast) Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons (Plastic) GMC Number: 4686602
- Ms Lyndsey Highton, BM BCh (Oxon) MA FRCS (Plast) GMC Number: 6128243
- Mr Philip Lim BSc (Hons), MB ChB, AFRCS (Ed), MRCS (Eng), FRCS (Plast) GMC Number: 4219068
- Mr Olubowale, MB ChB, MSc (Sheffield), FRCSI, FRCSI (Gen Surg) GMC Number 6044974
- Mr Maisam Fazel MA(Cantab) MB BChir MSEd FRCS GMC Number: 4767420
- Mr Mobinulla Syed MBBS, MSc, PhD, FRCS (Plast) GMC Number: 6035480
- Mr Prashant Govilkar, MBBS MS MCh FRCS FRCS (Plast) GMC Number: 4258041
- Mr Adel Fattah, FRCS (Plast.) GMC Number: 4764599
- Mr Kenneth Kok MBChB MRCS MSc(Hons) FRCS(plast) GMC Number: 4701147
To find out more about breast augmentation surgery or book to book a consultation please call 03339209135 or take a look at our comprehensive breast surgery website and breast enlargement video guides.